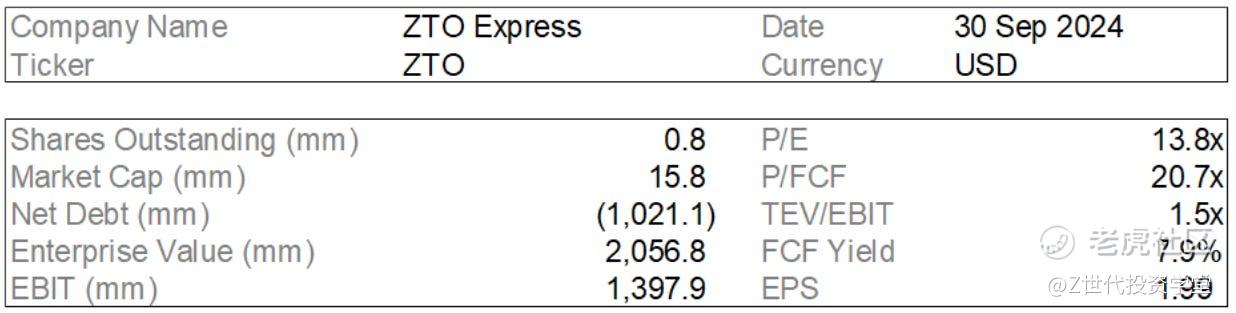
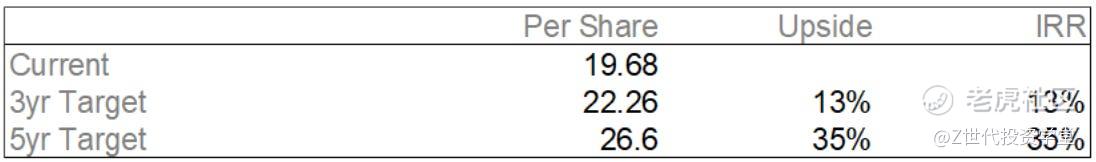
Executive Summary
Why ZTO Express?
ZTO Express was explored because it is one of the largest players in China’s logistics market and is renowned as a cost leader. Their proprietary "Zhongtian system" has significantly advanced their automation processes, giving them a strong technological edge. Additionally, China’s robust e-commerce growth and increasing demand for efficient logistics services make it an attractive market. This competitive advantage in automation and cost efficiency sets ZTO apart from other market players.
Company Overview
ZTO Express (Cayman) Inc. provides express delivery services and various value-added logistics solutions across the People's Republic of China. Leveraging a highly scalable network partner model, the company offers cost-effective express parcel delivery services. ZTO Express serves a diverse clientele, including e-commerce platforms, traditional businesses, and other express service users, ensuring extensive geographic reach at competitive rates.
Revenue Driver
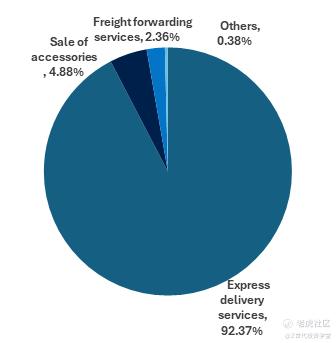
4 Main Categories of Products and Services: ZTO operates through 4 main business segments 1) Express delivery services, 2) Sale of accessories, 3) Freight forwarding, and 4) Others. Express delivery services accounts for the majority (92.37%) of the firm’s revenue.
High Revenue from Express Delivery Services: ZTO Express has the number 1 market share by parcel volume in China’s express delivery industry since 2016, delivering 30.2 billion Parcels in 2023.
Revenue is primarily driven by: Parcel volume and the network transit fee that ZTO charges their network partners for each parcel going through our network.
Highly Dependent on development of e-commerce industry and emergence of New Retail in China: more than 90% of total parcel volume was attributed to e-commerce.
Figure 1: Revenue breakdown of ZTO's different services
Cost Driver
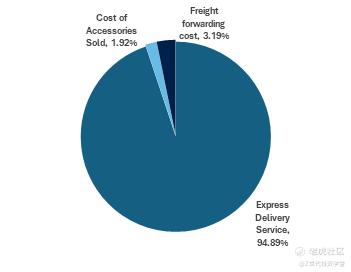
Express Delivery Services Cost includes: Line-haul transportation cost, sorting hub costs, and other costs of revenue (which include information technology-related costs, dispatching costs to network partners, etc).
Cost of Accessories Sold include: accessories that ZTO sells to their network partners
Freight Forwarding Cost relates to: Freight Forwarding services provided by China Oriental Express Co. Ltd which was previously acquired by ZTO.
Figure 2: Cost breakdown of ZTO key line items
Business Model
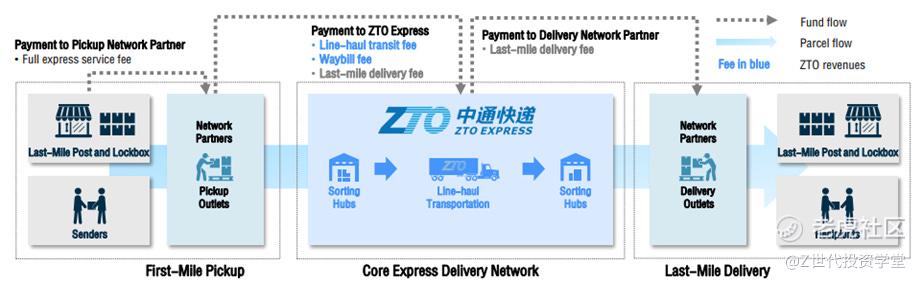
Figure 3: Taken from ZTO's quarterly announcement detailing overview of their business model
ZTO Operates a Network Partner Business Model: As of December 2023, ZTO has over 31,000 pickup/delivery outlets and over 6,000 direct network partners. ZTO utilises this network partners to directly interact and serve end customers.
Express Delivery Service Payment Breakdown: The full delivery fees collected by pickup outlets upfront from the senders comprise i) pickup service fees, ii) the network transit fee which is payable to ZTO and iii) the last-mile delivery fee payable to network partners who operate the delivery outlets and individual couriers.
Express Delivery Process:
i)Parcel Pickup: This is arranged through a network partner’s outlet, where a courier collects the parcel from the sender and forwards it to the regional sorting hub.
ii)Parcel Sorting and Line-Haul Transportation: Upon receiving parcels from various pickup outlets within its coverage area, the sorting hub processes, repacks, and dispatches them to the destination hubs. ZTO provides line-haul transportation between these hubs.
iii)Parcel Delivery: At ZTO’s destination sorting hub, parcels are unloaded, sorted, and subsequently delivered to recipients through delivery outlets operated by ZTO’s network partners.
Industry Overview
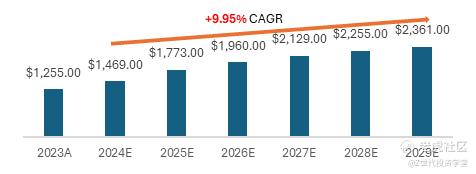
Figure 4: China's e-commerce gross merchandise value (Source: Statista)
China has the world’s largest e-commerce market. According to Statista, the market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.95% from 2024 to 2029, reaching a projected volume of $2,361 billion by 2029. The e-commerce penetration rate is anticipated to rise from 78.8% in 2024 to 97.4% by 2029.
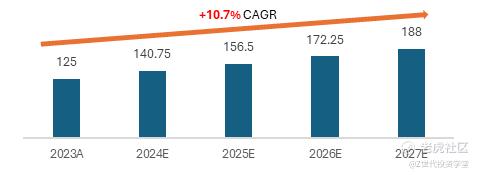
Figure 5: China's parcel delivery volume in million by express delivery providers (Source: Statista)
The rapid growth of e-commerce in China has significantly reshaped and accelerated the development of the logistics and express delivery sectors. Driven by strong e-commerce demand, supportive government policies, technological advancements, and increasing cross-border shipments, China’s express delivery market is projected to grow from 125 billion parcels in 2023 to 188 billion parcels by 2027, representing a CAGR of 10.7%.
Drivers of China's Express Delivery Market
Strong demand from e-commerce: Given that e-commerce accounts for most of the demand for express delivery, the continued rapid growth of e-commerce is expected to remain the primary driver of China's express delivery market.
Favourable government policies: China is supporting the e-commerce market by establishing a modern logistics infrastructure network with a total of 120 national logistics hubs and about 100 national major cold chain logistics bases in the next few years to come.
Technological Advancement: The adoption of new technologies and automation solutions in express delivery operations has accelerated. Innovations include unmanned technologies like drones and robot delivery vehicles, along with artificial intelligence to automate processes. These advancements enhance efficiency, improve service quality, and increase delivery capacity.
Rising demand for cross-border express delivery: Under China’s 14(th) Five Year Plan, the state plans to promote cross-border e-commerce via expansion of China’s e-commerce markets to overseas markets; connecting domestic producers and suppliers to consumers overseas.
Competitive Landscape
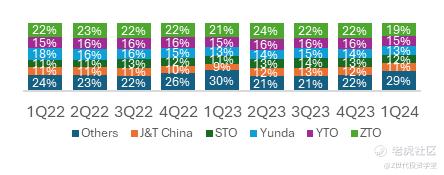
Figure 6: Market share split between express delivery providers in China by parcel volume deliveries (Source: ZTO Express Estimate)
Market Share: The express delivery market is oligopolistic, dominated by a few key players, but with a growing number of smaller competitors. ZTO leads the market with a 19% share in parcel volume as of the latest quarter. Together, the top five companies — J&T China, STO, Yunda, YTO, and ZTO — control 70% of the market. Despite this concentration, the number of smaller competitors has been increasing in recent quarters.
Porter's 5 Forces Analysis
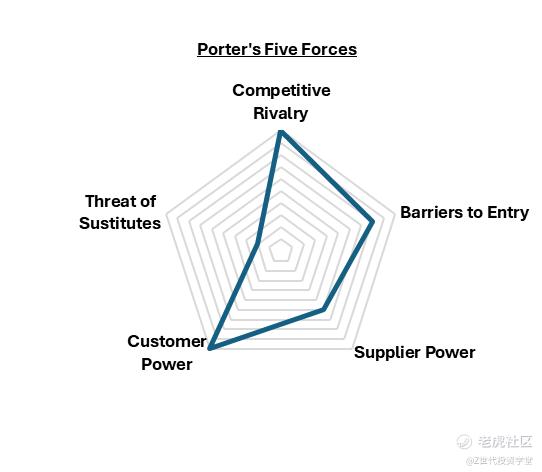
Figure 7: Porter's Five Forces overview
Barriers to Entry: The Chinese express delivery market has mid-to-high barriers to entry due to the high initial capital investment required to purchase and own their own fleet of delivery vehicles. Additionally, owning infrastructure such as warehouses and sorting facilities can add to costs. Investments in tracking systems and delivery management software also require capital.
Supplier Power: ZTO has moderate bargaining power over its suppliers (e.g. fuel providers, vehicle manufacturers), due to its ability to purchase in large quantities that can lower unit cost and hence purchasing prices. Furthermore, due to the firm’s size, ZTO sign long-term contracts with suppliers to secure favourable terms and pricing.
Customer Power: Customers have high bargaining power. Customers in this market tend to be very price sensitive, meaning that high prices might end up causing customers to switch brands to enjoy more competitive prices. This makes it paramount for ZTO to optimise operations to enjoy savings in line-haul transportation and sorting costs, leverage economies of scales and explore other cost savings methods to lower their Average Selling Price (ASP).
Competitive Rivalry: Highly competitive, numerous oligopolies (YTO Express, STO Express, Yunda) vying for market share. Price competition is also intense, as firms try to undercut one another with price wars. In addition to pricing strategies, firms also compete on service quality, delivery speed, and other differentiating factors to stand out in the crowded marketplace.
Threat of Substitutes: Low threat of substitutes. While traditional postal/delivery services and self-delivery exist, they do not offer the same speed and convenience as express delivery services.
Competitor Analysis
The competitors including ZTO are collectively known as the "Tongda Operators", where they represent the top five national express delivery companies that adopt the network partner model. Each player provides line-haul transportation, sorting, and waybill services to its network partners in exchange for fees, while their local network partners provide first-mile pickups and last-mile delivery services under the Tongda’s brand and collect customer payment. Notably, J&T Express is the latest entrant into the space, having been founded in 2015, acting as a logistics service provider specialising in express delivery business for major e-commerce platforms such as Alibaba and Pinduoduo. Despite being new to the market, they have captured circa 11% of the market share within three years of entering the Chinese market through an aggressive merger & acquisition strategy of acquiring smaller network and infrastructure players, including Bext Express and Fengwang Express to strengthen their business distribution network in China.
Comparision of the Network
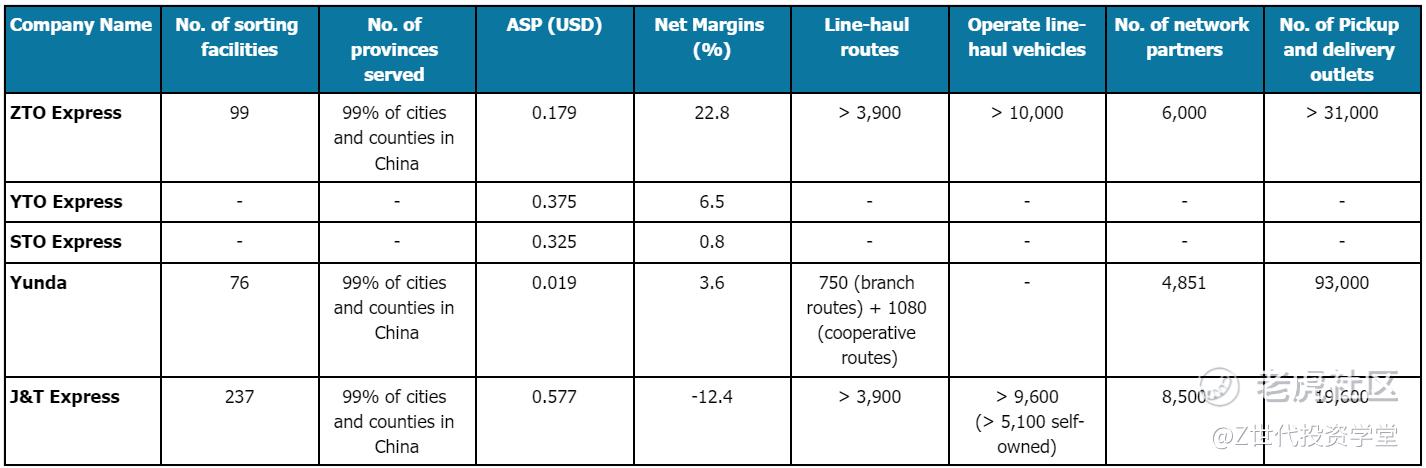
Figure 8: Average selling price, sorting facilities and fleet capacity of Tongda Operators. (Source: Company's Annual Report and Investor Relations)
*Do note that all of this is for information only and should not be taken as investment advice. If you should choose to invest in any of the stocks, you do so at your own risk.
*请注意,所有这些仅供参考,不应被视为投资建议。如果您选择投资任何股票,您需要自行承担风险。


精彩评论