
Competitor Analysis
TSMC crafted and maintained its market position by focusing its business model solely on the production of semiconductors. However, the semiconductor industry is very segmented with fabless companies designing the chipsets and foundries manufacturing the final product. While some companies choose to become IDMs to design and manufacture their own chips, TSMC decided not to manufacture any products under its own name, so that the company never engages in direct competition with its customers.
The competition in the semiconductor foundry industry is fierce as TSMC competes with other foundry service providers and some Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs). However, as chip designs grew increasingly complex, requiring specialized manufacturing skills, TSMC and Samsung emerged as the only companies with the necessary expertise. Samsung, despite its capabilities, faced challenges. Firstly, its dual role as a chip designer led many advanced designers to doubt its impartiality due to the competitive nature of relationship between design houses and IDM-based foundries. Next, its lower yield rates and poor chip performance meant customers often paid for non-functional chips, driving its customers towards its competitors. For example, while Samsung may be the first to transition to GAAFET for its 3nm chips, it faces challenges in scaling up its capabilities due to poor yield and low adoption rates. Consequently, seven tech giants, including Nvidia, AMD, Intel, Qualcomm, MediaTek, Apple and Google, have decided to use TSMC’s 3nm process. Therefore, TSMC became the preferred choice for manufacturing the most advanced chips.
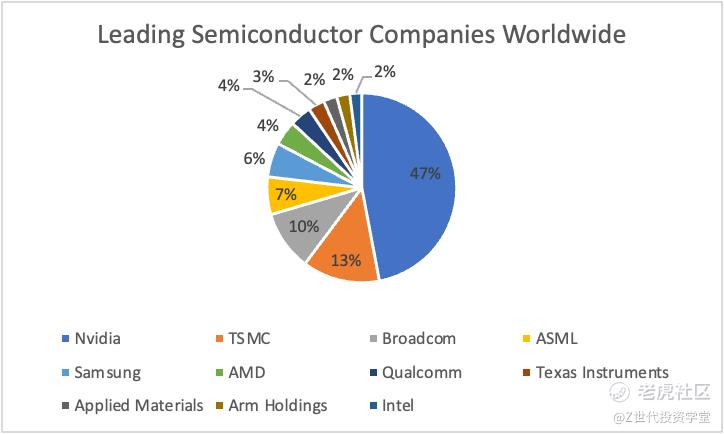
Figure 2 shows that TSMC is the second largest semiconductor company worldwide and has a 13% market share.
Focusing solely on chips manufacturing, TSMC is the world’s largest producer of semiconductors and the main supplier for large-tech companies. TSMC dominates the market with 53% share in chip manufacturing and over 91% share in advanced chip manufacturing, serving as the exclusive manufacturer for tech giants like Apple and Nvidia. Despite IDMs having their own foundry capabilities, Intel relies on TSMC for its cutting-edge chip production, highlighting the intricate dynamics of the chip manufacturing industry, where expertise, trust, and reliability play critical roles in shaping market dominance and technological advancement.
Economic Moat
-
High Capital Intensity and Cost Barrier
TSMC operates in an industry that requires immense capital investment. For instance, equipment like the Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography (EUV) machine is essential for advanced semiconductor manufacturing but costs around $150 million per unit. This creates a significant barrier to entry for competitors who must also invest heavily to compete at TSMC's level. Moreover, securing these machines is difficult due to high demand and limited supply, further solidifying TSMC's advantage.
-
Complexity in Operations
Operating advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment like the EUV machine requires specialized knowledge, extensive training, and ongoing investment in maintenance and upgrades. The complexity and high operational costs act as a deterrent for potential competitors looking to enter or expand in this market.
-
Established Manufacturing Expertise
TSMC has developed a highly sophisticated manufacturing process that spans multiple intricate steps beyond lithography, such as wafer preparation, etching, doping, metallization, and packaging. Coordinating and optimizing these processes require deep expertise and experience, which TSMC has accumulated over decades. This expertise is not easily replicated, giving TSMC a significant operational advantage.
-
Customer Trust and Relationship
TSMC serves major semiconductor companies that design cutting-edge chips. These customers value reliability, quality, and consistency in production, factors that TSMC has proven itself capable of delivering. Switching foundries involves substantial risk and disruption, which makes customers reluctant to change suppliers unless there is a compelling reason. TSMC's long-standing relationships and reputation as a dedicated foundry further strengthen its moat.
-
Limited Competition at TSMC's Level
In the advanced semiconductor manufacturing space, TSMC faces limited direct competition. Samsung is its closest competitor, but both companies dominate due to their immense scale, technological prowess, and financial strength. This duopoly, with TSMC as the leading dedicated foundry, further consolidates its position in the market.
Investment Theses
-
TSMC stands out as an industry leader for its production of cutting-edge technology.
TSMC has consistently prioritized the development of robust, internal R&D capabilities. As a prominent leader in global semiconductor technology, TSMC offers the most cutting-edge and extensive range of dedicated foundry process technologies. In 2022, TSMC initiated high-volume production of its 3nm FinFET (N3) technology, representing the industry's most advanced semiconductor technology with superior power, performance, and area (PPA) compared to its 5nm predecessor.
TSMC has introduced advanced versions of its N3 technology, including N3E and N3P, aimed at enhancing power, performance, and density. N3E began mass production in late 2023, and TSMC plans to further expand its 3nm technology family with N3X for high-performance computing and N3AE for automotive applications.
Increased US restrictions on China's access to advanced chip technology and Samsung's challenges with 3nm GAA yield rates have highlighted TSMC's dominant position. Major tech firms like NVIDIA, AMD, Intel, Qualcomm, MediaTek, Apple, and Google are shifting to TSMC's 3nm process despite rising prices.
Concurrently, TSMC is also developing its 2nm (N2) technology, featuring nanosheet transistors, with volume production expected in 2025. This new technology aims to set industry benchmarks in density and energy efficiency, reinforcing TSMC's leadership in semiconductor technology.
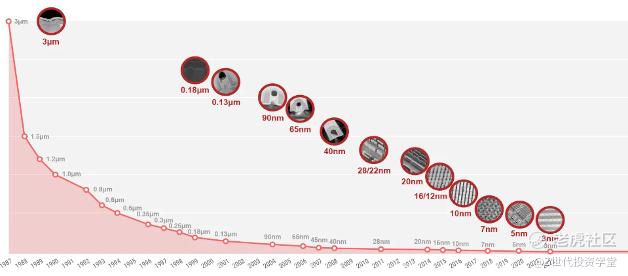
Figure 3 above shows the rapid development of smaller chips in recent years, emphasizing the continuous need to innovate.
-
TSMC's role as the largest pure-play foundry allows it to collaborate with both IDMs and design houses.
Although Broadcom operates as an IDM, it is also a customer of TSMC. Broadcom's AI-related revenue is expected to more than triple in the next few years, increasing from $4.2 billion in 2023 to $14 billion in 2025, accounting for 39% of the company's total semiconductor revenue. As one of the largest customers of TSMC, Broadcom's growth in AI-related revenue will benefit TSMC substantially.
To maintain its competitive edge in manufacturing chips with high performance yield, TSMC continues to invest heavily in R&D, spending $5.856 billion in 2023. This investment surpasses that of Broadcom, which spent $5.253 billion, and Samsung, which invested $2.273 billion.
-
The US Chips Act provides financial support to TSMC as it invested over $65 billion into three new chip factories in Arizona.
In a bid to attract semiconductor manufacturing back to the United States after its share of global chip fabrication capacity declined from about 40% in 1990 to around 12% in 2020, the Creating Helpful Incentives to Produce Semiconductors and Science Act of 2022 (the "U.S. CHIPS Act") offers financial incentives aimed at fostering the growth of the semiconductor industry within the United States.
In April 2024, TSMC announced today that the U.S. Department of Commerce has entered into a preliminary memorandum of terms (PMT) with TSMC Arizona, outlining potential direct funding of up to US$6.6 billion under the CHIPS and Science Act. Concurrently, TSMC revealed plans to construct a third fabrication facility at its Arizona site to meet robust customer demand, utilizing the most advanced semiconductor process technology available in the United States.
Therefore, the CHIPS and Science Act facilitates an unprecedented investment opportunity by enabling TSMC to provide cutting-edge manufacturing capabilities within the United States. TSMC’s operations in the United States will strengthen support for American customers, including leading global technology firms, and enhance its ability to drive future innovations in semiconductor technology.
Valuation
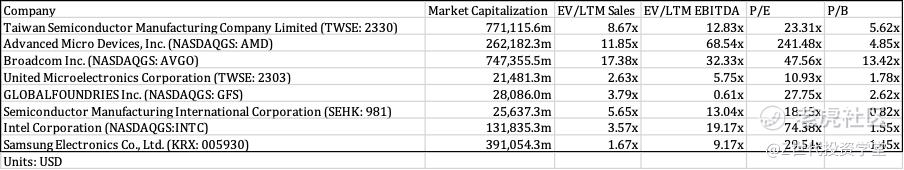
These peer companies were chosen as they are either foundries or as they that manufacture semiconductors. However, most of the peer companies are much smaller than TSMC with only Broadcom Inc. being of a comparable size. It is also notable that 40% of the growth comes from the top 4 largest semiconductor companies, namely Nvidia, TSMC, Broadcom and Qualcomm. Given that the larger cap companies experience a higher EV/LTM Sales, I took the best case scenario to forecast TSMC’s revenue.
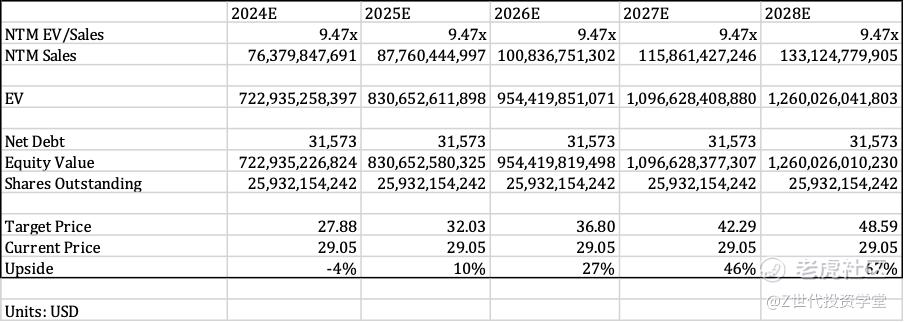
I recommend a HOLD for TSMC, setting a 1 year price target of $27.88, and a 5 year price target of $48.59. Given that TSMC is slightly inflated after riding on the exponential revenue growth experienced by Nvidia, TSMC’s stock price could take a hit in 2024. However, I believe that the stock price will rebound in subsequent years due to the investment theses mentioned above.
*Do note that all of this is for information only and should not be taken as investment advice. If you should choose to invest in any of the stocks, you do so at your own risk.

精彩评论