TABLE OF CONTENTS
• What Is Earnings Per Share (EPS)?
• Formula and Calculation for EPS
• Example of EPS
• Formula and Calculation for EPS
• Why EPS Is Important
• Basic EPS vs. Diluted EPS
• EPS Excluding Extraordinary Items
What Is Earnings Per Share (EPS)?
Earnings per share (EPS) is calculated as a company's profit divided by the outstanding shares of its common stock. The resulting number serves as an indicator of a company's profitability. It is common for a company to report EPS that is adjusted for extraordinary items and potential share dilution.
The higher a company's EPS, the more profitable it is considered to be.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
• Earnings per share (EPS) is a company's net profit divided by the number of common shares it has outstanding.
• EPS indicates how much money a company makes for each share of its stock and is a widely used metric for estimating corporate value.
• A higher EPS indicates greater value because investors will pay more for a company's shares if they think the company has higher profits relative to its share price.
• EPS can be arrived at in several forms, such as excluding extraordinary items or discontinued operations, or on a diluted basis.
Earnings Per Share Explained
Formula and Calculation for EPS
Earnings per share value is calculated as net income (also known as profits or earnings) divided by available shares. A more refined calculation adjusts the numerator and denominator for shares that could be created through options, convertible debt, or warrants. The numerator of the equation is also more relevant if it is adjusted for continuing operations.
To calculate a company's EPS, the balance sheet and income statement are used to find the period-end number of common shares, dividends paid on preferred stock (if any), and the net income or earnings. It is more accurate to use a weighted average number of common shares over the reporting term because the number of shares can change over time.
Any stock dividends or splits that occur must be reflected in the calculation of the weighted average number of shares outstanding. Some data sources simplify the calculation by using the number of shares outstanding at the end of a period.
Example of EPS
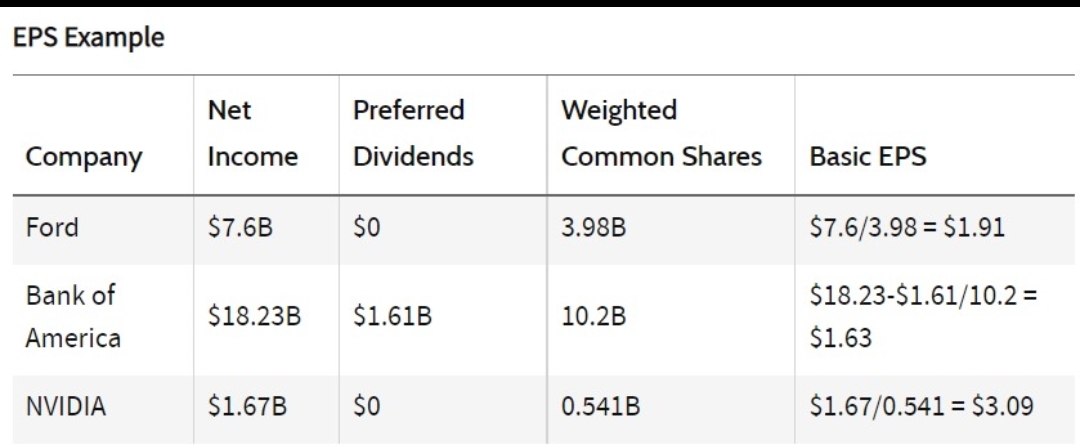
Say that the calculation of EPS for three companies at the end of the fiscal year was as follows:
EPS Example
Company Net Income Preferred Dividends Weighted Common Shares Basic EPS
Ford $7.6B $0 3.98B $7.6/3.98 = $1.91
Bank of America $18.23B $1.61B 10.2B $18.23-$1.61/10.2 = $1.63
NVIDIA $1.67B $0 0.541B $1.67/0.541 = $3.09
How Is EPS Used?
Earnings per share is one of the most important metrics employed when determining a firm's profitability on an absolute basis. It is also a major component of calculating the price-to-earnings (P/E) valuation ratio, where the E in P/E refers to EPS. By dividing a company's share price by its earnings per share, an investor can see the value of a stock in terms of how much the market is willing to pay for each dollar of earnings.
EPS is one of the many indicators you could use to pick stocks. If you have an interest in stock trading or investing, your next step is to choose a broker that works for your investment style.
Comparing EPS in absolute terms may not have much meaning to investors because ordinary shareholders do not have direct access to the earnings. Instead, investors will compare EPS with the share price of the stock to determine the value of earnings and how investors feel about future growth.
Basic EPS vs. Diluted EPS
The formula in the table above calculates the basic EPS of each of these select companies. Basic EPS does not factor in the dilutive effect of shares that could be issued by the company. When the capital structure of a company includes items such as stock options, warrants, or restricted stock units (RSU), these investments—if exercised—could increase the total number of shares outstanding in the market.
To better illustrate the effects of additional securities on per-share earnings, companies also report the diluted EPS, which assumes that all shares that could be outstanding have been issued.
For example, the total number of shares that could be created and issued from NVIDIA's convertible instruments for the fiscal year that ended in 2017 was 23 million. If this number is added to its total shares outstanding, its diluted weighted average shares outstanding will be 541 million + 23 million = 564 million shares. The company's diluted EPS is, therefore, $1.67 billion /.564 million = $2.94.1
Sometimes an adjustment to the numerator is required when calculating a fully diluted EPS. For example, sometimes a lender will provide a loan that allows them to convert the debt into shares under certain conditions. The shares that would be created by the convertible debt should be included in the denominator of the diluted EPS calculation, but if that happened, then the company wouldn’t have paid interest on the debt. In this case, the company or analyst will add the interest paid on convertible debt back into the numerator of the EPS calculation so the result isn’t distorted.
精彩评论